What is KNN?
KNN categorizes new values into the category that has a majority among the K nearest neighbors.
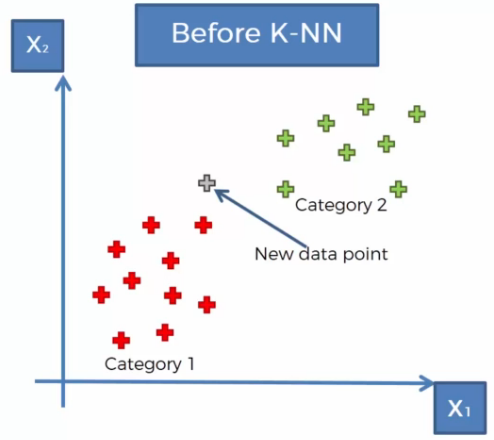
To
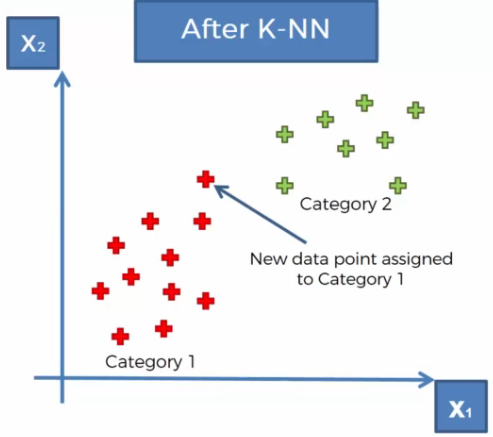
Steps of KNN
- Step 1.
Choose the number K of neighbors.
Let’s assume that K is 5.
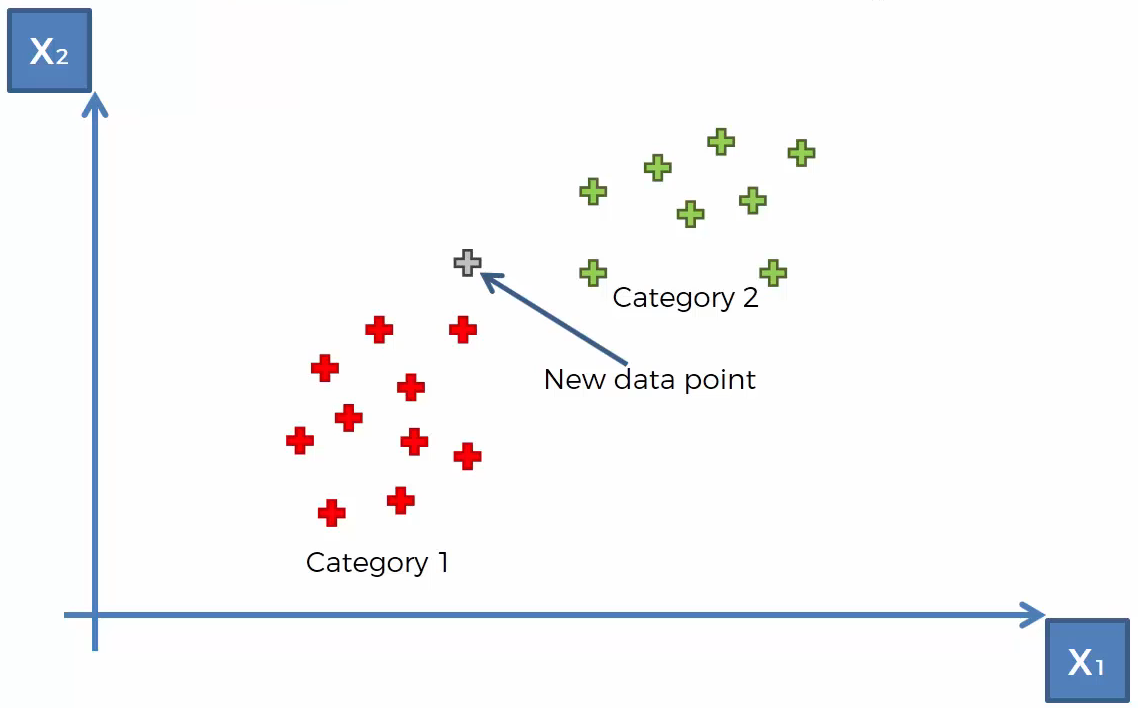
- Step 2.
Take the K nearest neighbors of the new data point according to the Euclidean distance (most commonly used), Manhattan distance, or any other distance metric.
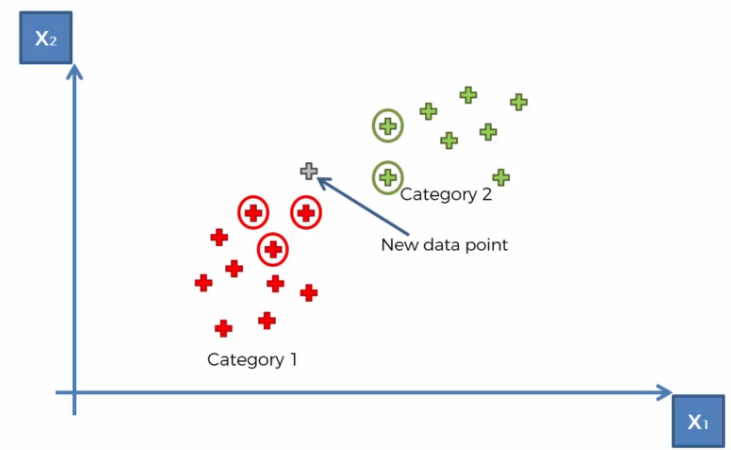
- Step 3.
Among these K neighbors, count the number of data points in each category.
In the example:- Category 1: 3 neighbors
- Category 2: 2 neighbors
- Category 1: 3 neighbors
- Step 4.
Assign the new data point to the category with the most neighbors.
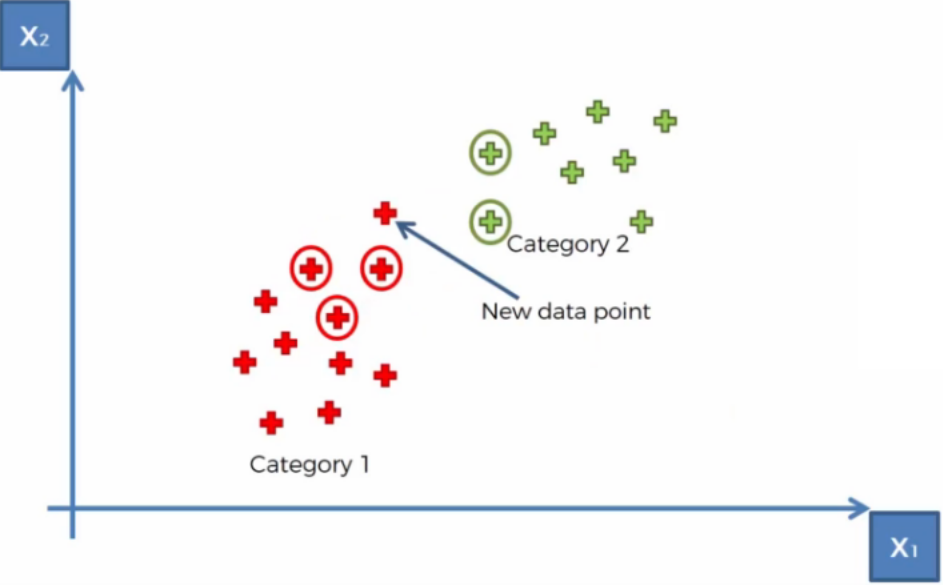
Example
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5, metric='minkowski', p=2) #metric : algorithm to determine the distance between two points.
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
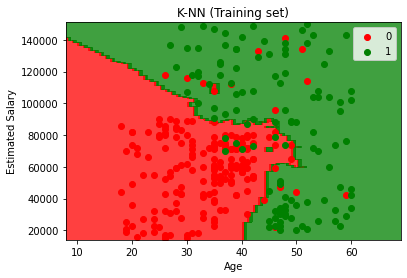
Result